Understanding Eczema: Causes, Symptoms, Stages, and Treatment Approaches
Introduction
Introduction
Hello, I’m Dr. Karma Patel, a dermatologist with a special interest in teledermatology. Through online dermatology consultations, we have helped many patients manage eczema effectively with personalized treatment plans.
If you are searching for eczema causes, eczema symptoms, or the best online eczema treatment for hands and face, this guide is written to answer exactly what you are looking for.
In this blog, you will learn what causes eczema, how eczema starts, its stages, common triggers, and dermatologist‑approved treatment options that actually work.
What Is Eczema?
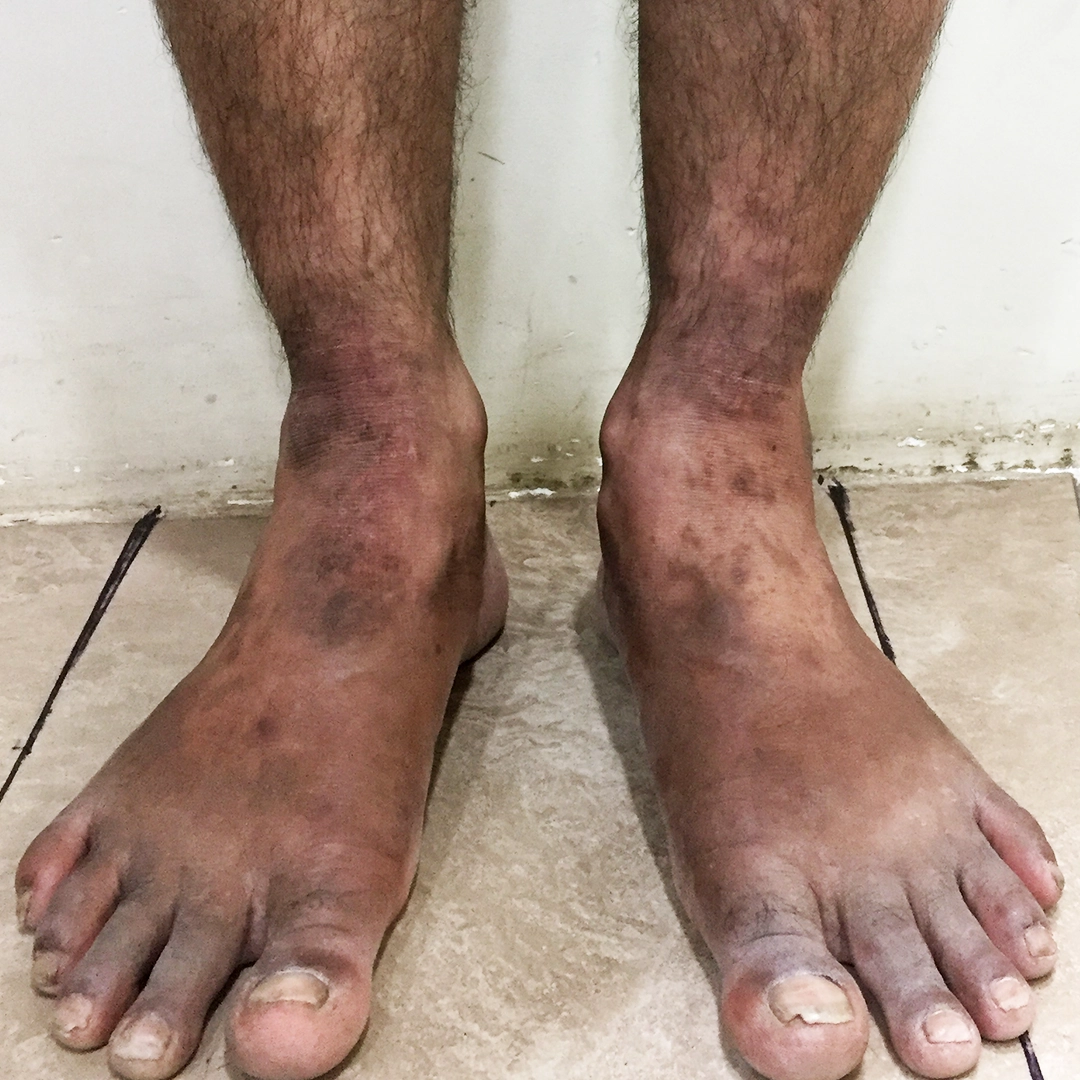
Eczema is a chronic inflammatory skin condition marked by itching, redness, dryness, oozing, and crusting. It often follows a relapsing course, meaning symptoms can improve and worsen over time.
Many patients ask why eczema occurs and how eczema occurs. In simple terms, eczema develops due to a combination of skin barrier dysfunction, immune system overactivity, and exposure to triggers.
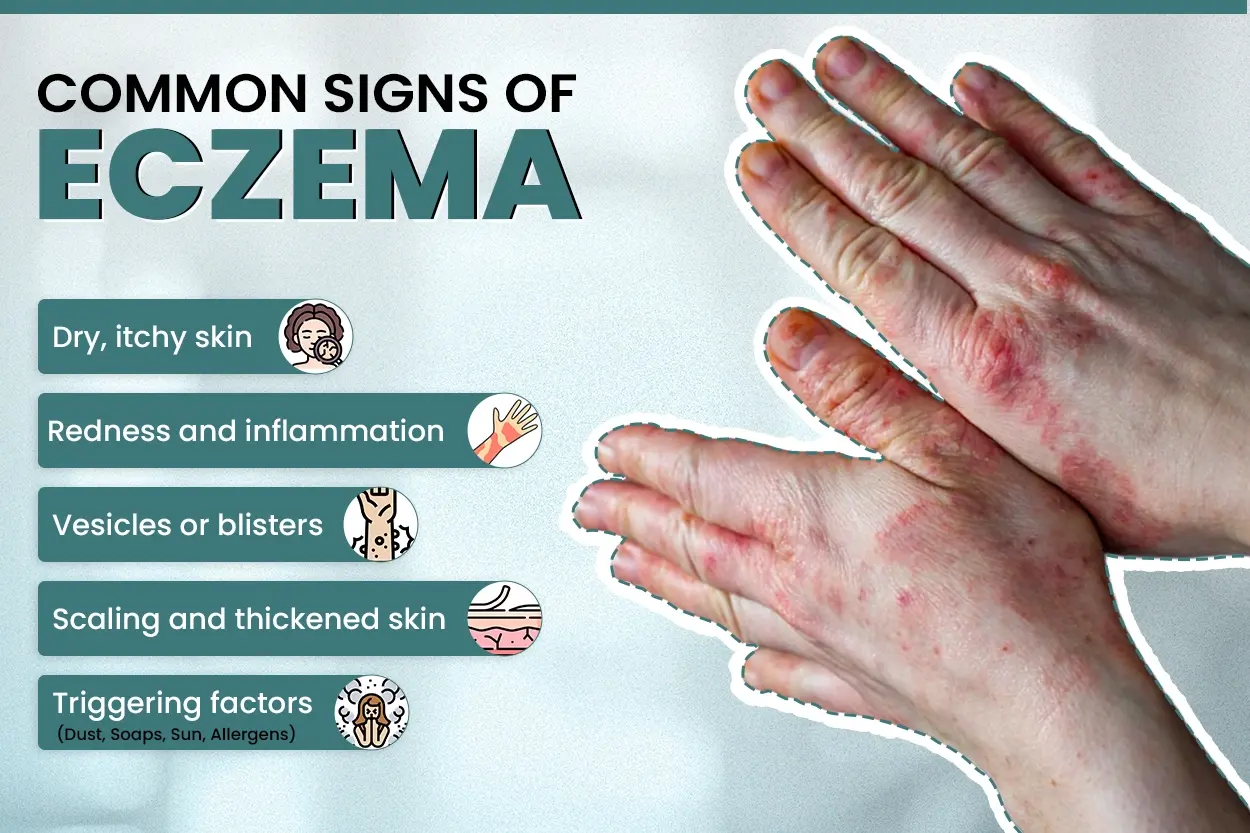
Eczema Symptoms You Should Not Ignore
Common eczema symptoms include:
- Persistent itching (often worse at night)
- Red or inflamed patches of skin
- Dry, scaly, or cracked skin
- Oozing or crust formation during flare‑ups
- Thickened, leathery skin in chronic cases
Early identification of eczema symptoms helps prevent severe flare‑ups and long‑term skin damage.
- Red, swollen plaques
- Tiny fluid‑filled blisters (vesicles)
- Severe itching and oozing
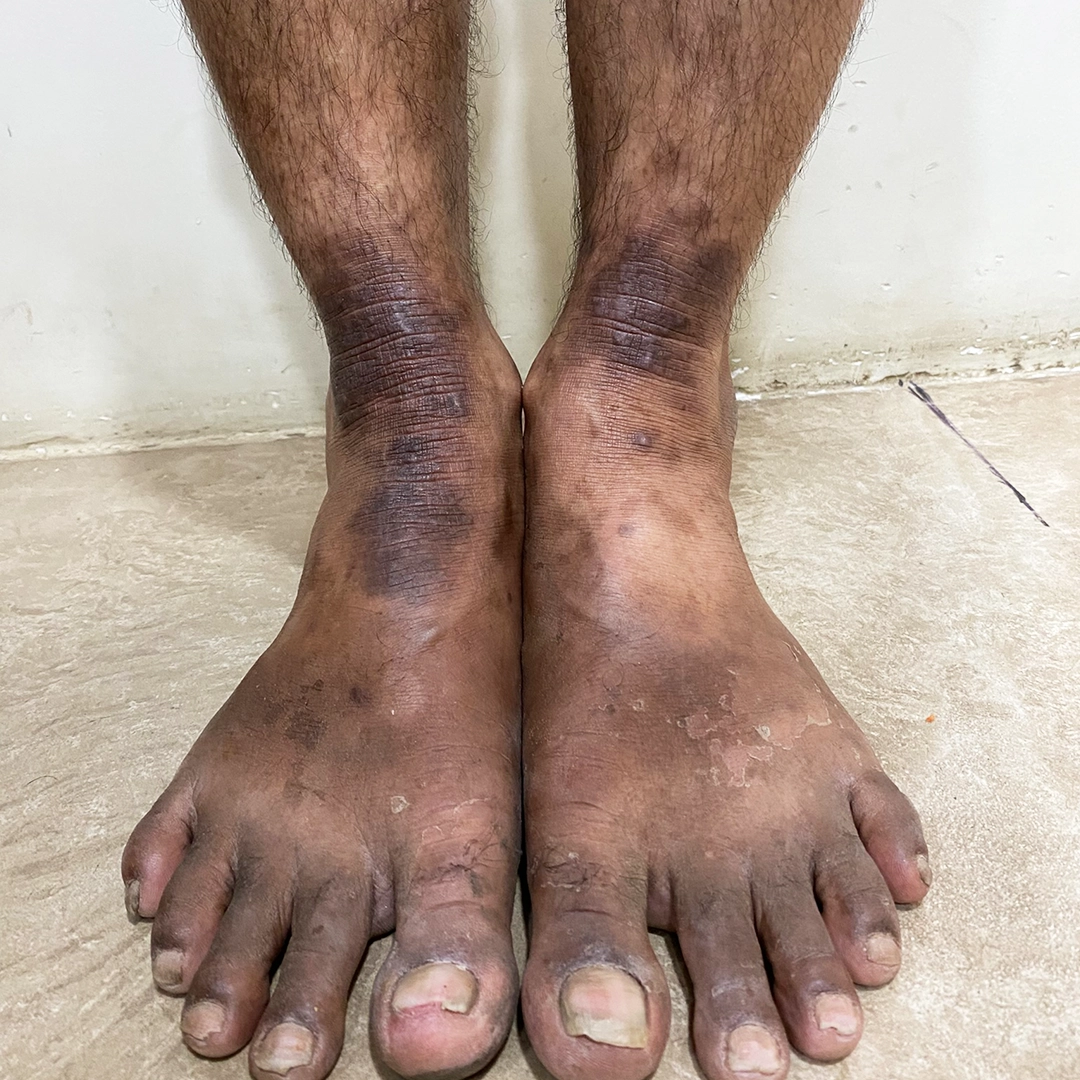
- Reduced oozing
- Persistent redness
- Scaling and dryness
- Thickened skin (lichenification)
- Darkened skin tone
- Intense itching due to repeated scratching
What Causes Eczema?
Patients frequently ask what eczema causes, how eczema starts, and eczema causes due to what factors. Eczema is not caused by a single factor but by multiple internal and external triggers.
Common Eczema Causes:
- Dust, plants, and grass
- Harsh soaps and detergents
- Cement and construction materials
- Chemicals and allergens
- Sun exposure
- Climate changes
- Certain foods (in susceptible individuals)
What Causes Eczema on the Face?
Facial eczema is commonly triggered by:
- Cosmetic products
- Fragrances and preservatives
- Sun exposure
- Frequent face washing
- Air pollution
Types of Eczema: Exogenous vs Endogenous
Eczema is a broad term, and based on the nature of the etiological agent, it is classified into exogenous and endogenous. Some of the examples of exogenous eczema and endogenous eczema are given below:
Exogenous Eczema: (caused by external factors):
- Irritant Contact Eczema: Caused by direct skin contact with irritants like soaps, detergents, or chemicals.
- Allergic Contact Eczema: Triggered by an allergic reaction to substances such as metals, fragrances, or plants.
- Infective Eczema: Occurs when existing eczema becomes secondarily infected with bacteria, viruses, or fungi.
- Post-Traumatic Eczema: Develops in areas of skin injury or repeated friction, leading to chronic inflammation.
Endogenous Eczema: (linked to internal or genetic factors):
- Atopic Dermatitis: A chronic, relapsing form of eczema often associated with a family history of allergies or asthma.
- Discoid Eczema: Characterized by coin-shaped patches of inflamed, itchy, and dry skin.
- Pompholyx: A form of eczema affecting the hands and feet, presenting with small, itchy blisters.
- Venous Eczema: Occurs in the lower legs due to poor circulation or varicose veins, leading to red, scaly patches.
We shared another blog to know about the Nummular Eczema vs Ringworm: How to Identify and Treat the Right Condition.
Now, let us come to the most important part of this blog, which is eczema treatment options
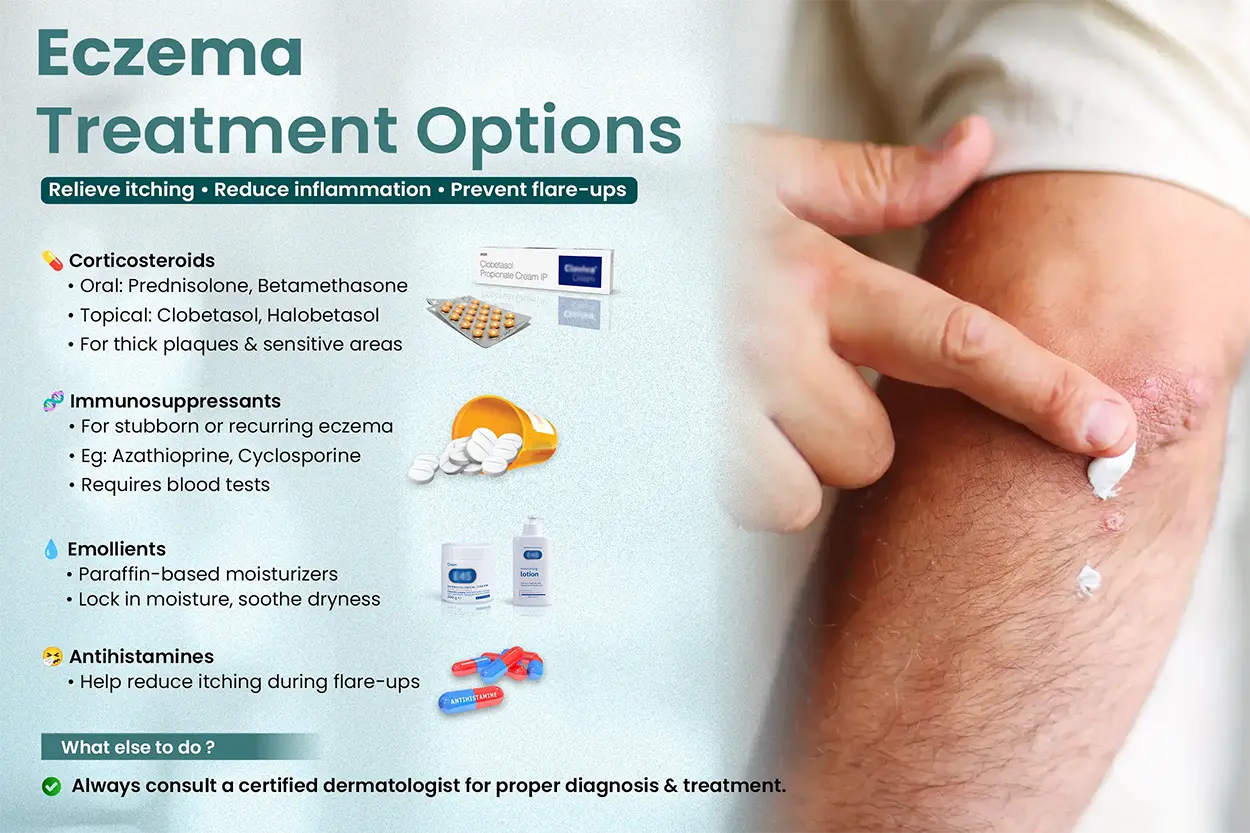
Eczema Causes and Treatment: Dermatologist‑Recommended Options
Eczema treatment focuses on controlling inflammation, relieving itching, repairing the skin barrier, and preventing recurrence.
1. Corticosteroids (Topical and Oral)
Corticosteroids, oral as well as topical, are the mainstay of the treatment of eczema.
- Oral corticosteroids such as prednisolone, methylprednisolone, betamethasone, dexamethasone, & deflazacort are regularly prescribed by dermatologists.
- Topical corticosteroids such as clobetasol and halobetasol are used for thick plaques.
- Corticosteroids exert anti-inflammatory, anti-proliferative, vasoconstrictive, & immunosuppressive effects.
- It helps to reduce inflammation.
- Topically, high-potency corticosteroids such as halobetasol and clobetasol are used to treat the thick plaques of eczema.
- Low to moderate potency corticosteroids are used in eczema treatment on areas with thin skin.
2. Antihistamines
- Antihistamines are given as a supportive treatment that helps to reduce itching. Especially during acute flare-ups.
3. Emollients and Moisturizers
- Emollients containing liquid paraffin and white soft paraffin are frequently prescribed along with topical corticosteroids in eczema treatment.
- Emollients help to decrease transepidermal water loss and keep the stratum corneum (outermost layer of the epidermis) hydrated.
- It helps to reduce dryness and itching.
4. Immunosuppressants
- Other immunosuppressive agents such as azathioprine and cyclosporine are also used in case of recurrences and in case the patient does not respond to oral corticosteroids.
- Being a practitioner in clinical dermatology, it is advisable to carry out necessary blood investigations before putting patients on this group of immunosuppressants.
- Knowing the triggering agent is an important part in eczema treatment.
- If you suspect the triggering agent for your eczema, avoiding contact with it is crucial, as eczema is a relapsing condition.
- If you suspect that itching is aggravated on exposure to any of the exogenous agent,s such as dust, plants, sun, chemicals, soap, cement, etc., covering exposed areas of the body will certainly help as it protects you from direct contact of that part of your body to the causative agent.
- In cases where you suspect that the triggering factor is the sun, then you should use sunscreen on a regular basis, especially when you go out in the sun.
- This helps you protect your skin from the sun.
- Patch testing helps in identifying the etiological agent.
Is Eczema Contagious? A Dermatologist’s Opinion
One of the most common questions I hear during online consultations is:
“Will eczema spread to others?” or “Can I pass eczema to my family through touch?”
The Clear Medical Answer
No. Eczema is not contagious.
Eczema does not spread through:
- Touching the affected skin
- Sharing clothes, towels, or bedding
- Physical contact, handshakes, or hugs
Unlike fungal or bacterial infections, eczema is not caused by germs that transfer from person to person. It is an inflammatory condition related to skin barrier weakness and immune response, not infection.
Why Patients Often Think Eczema Is Contagious
During consultations, patients commonly share concerns such as:
- Fear of touching their children or partners
- Avoiding social contact due to visible skin lesions
- Confusing eczema with fungal infections because of redness and itching
- Worry that scratching will “spread” eczema to other body parts
- These fears are understandable - but medically incorrect.
Dermatologist’s Advice for Patients
From my experience, reassurance and correct diagnosis make a huge difference. If you or your family member has eczema:
- Do not isolate yourself socially
- Do not stop physical contact out of fear
- Focus on correct treatment and trigger avoidance
Consult a dermatologist if symptoms worsen or change. Early guidance helps prevent complications and unnecessary anxiety.
Key Takeaway
✔ Eczema is not contagious
✔ It cannot spread to others through touch
✔ Visible symptoms do not mean infection
✔ Proper treatment controls flare-ups effectively
If you are unsure whether your skin condition is eczema or something infectious, a dermatologist consultation - especially online - can provide clarity and peace of mind.
Need Help with Eczema?
If you are concerned about your eczema and looking for eczema treatment, on hands, or face treatment, then, being a dermatologist, I would recommend that you consult a dermatologist online on neodermatologist.com, because a dermatologist is someone who is certified and specialized to treat your eczema and give valuable advice on:
- Which eczema cream or eczema ointment is good for your condition
- What eczema cream is best for your treatment
- How to find the etiological agent for your eczema through the required investigations
Explore Our Other Online Skin & Hair Services
If you're dealing with other skin or hair concerns, we offer more than just eczema solutions. You can explore our specialized dermatologist services like:
- Online Hair Loss Treatment
- Acne Treatment Online
- General Skin Consultation
- Fungal Jock Itch Treatment
Receive expert advice from experienced dermatologists, all through our convenient online platform.
Conditions We Also Treat
We also provide targeted treatments for conditions such as:
- Ringworm
- Scabies
- Psoriasis
- Urticaria (Hives)
- Vitiligo
Our online consultation platform makes it easy to access the care you need, right from the comfort of your home.
To know more about Free Online Dermatology Consultation
Click on the link - Get a free skin online photography consultation with a dermatologist.
Conclusion
Eczema can be frustrating, but with the right understanding of eczema causes, symptoms, stages, and treatment, it can be effectively controlled. Early diagnosis, trigger avoidance, and dermatologist‑guided treatment are the keys to long‑term relief. If your eczema keeps recurring or is affecting your quality of life, do not delay professional care. Online dermatologist consultation makes expert eczema treatment accessible, safe, and effective.
Read this page in Hindi → एक्जिमा को समझना: कारण, लक्षण, प्रकार और ऑनलाइन इलाज के विकल्प
MD (Dermatology) | Registration No.: G-53014
A dermatologist specializing in online consultations for skin, hair, and nail concerns. Offers expert care for acne, pigmentation, eczema, scabies, ringworm, scalp infections, dandruff, psoriasis, vitiligo, hives, and hair loss, providing effective, personalized treatment solutions from the comfort of home.
 Hin
Hin En
En


















Comments
Nishra Patel
Very informative and easy to understand article. It clearly explains what eczema is, its causes, symptoms, and available treatments. Helpful for anyone trying to manage or learn more about this condition.
सोमपाल गंगवार
मुझे 30 35 साल से सोरायसिस है दो-तीन दिन में अचानक कोई खंडन बिगड़ने के कारण ड्राई फ्रूट साबुन से नहाना कद्दू बीज कद्दू के बीज सनफ्लावर भी और मेथी दाना क्या दिखाया अंडे का भी सेवन रोज करते हैं पता नहीं किस वजह से इतनी एलर्जी हो गई है कि रात को चढ़ाने पड़ रहा है पूरे शरीर पर बहुत लाल धब्बे और चिकने हैं खुजली बहुत लगती है तो सब क्या करें
Nisha Singh
Boht achese eczema ke baare me samjaya he. Mujhe jo bhi doubt the sab kuch clear hogya yah blog padh kar.
Akshay Patel
This blog gave me a much clearer understanding of eczema - especially the part about identifying different triggers and treatment options. I’ve been struggling with flare-ups, and now I feel more confident about managing them better. Thank you for breaking it down so simply!
Post a comment